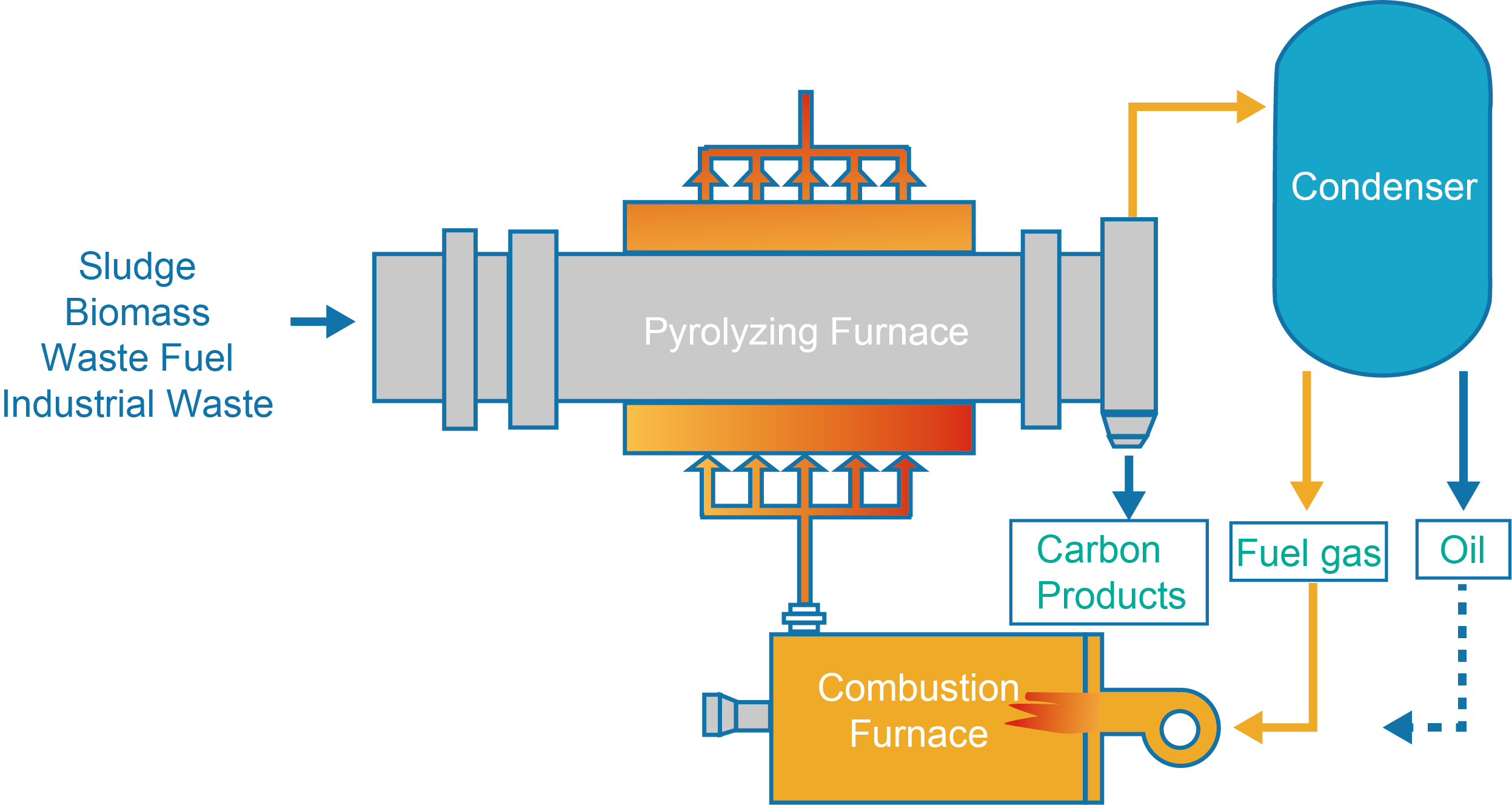
PYROLYSIS
Background
Thermochemical treatment technology is essential in organic solid waste quantity reduction and energy conversion. Traditional waste thermochemical treatment technology mainly includes incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis.
Advantages, disadvantages, and scope of application of 3 thermochemical treatment technologies:
Technology
Advantages
Disadvantages
Application
● Large capacity, high speed, and small footprint.
● Highest reduction rate and complete processing.
● High investment & operation costs, low utilization rate.
● High secondary pollution by fly ash and dioxin.
● Large-scale centralized waste disposal, minimum 500 tpd MSW.
Gasification and Incineration
● Controllable flexible scale.
● Wide application range.
● Low calorific value syn-gas.
● High investment & operation cost, low
resource utilization efficiency.
● Secondary pollution by fly ash and dioxin.
● Similar to incineration but with better pollution control. Suitable for medium-scale
plants.
● Flexible for power generation or low-quality heat
energy.
Pyrolysis
carbonization
● Controllable flexible scale.
● Low investment, wide application range.
● Small flue gas flow, no dioxin and secondary pollution. Considerable quantity &
volume reduction.
● Per-ton investment equal to incineration or gasification.
● Preheat drying required for over
30% moisture wastes.
● Suitable for small and
medium-sized waste disposal.
● Power generation.
● High-value-added products.
● The larger scale, the better benefit.
Power generation.
JADE compared to traditional pyrolysis technology
|
Pyrolysis Technology |
JADE Pyrolysis |
Traditional Pyrolysis |
|
Syngas quality |
Calorific value 15-17 MJ/KG. 2 - 3 times of syngas from traditional pyrolysis gasifiers.
|
Caloric value 4-7 MJ/KG. |
|
Tar reforming |
Tar reformed, solved the tar problem thoroughly. More stable operation. |
Can not solve tar blockage problem completely.
Unstable operation.
|
|
Flue gas treatment |
Avoid fly ash and dioxins secondary pollution of flue gas by purification and reforming. Low investment in flue gas treatment.
|
Syn-gas usually not purified prior to burning in the 2nd combustion chamber. Requires many process in flue gas treatment.
|
|
Energy utilization |
Optimized utilization of the system's high-temperature sensible heat, high heat treatment efficiency, highly efficient energy usage, and low operation energy consumption. |
Low efficiency energy usage. Requires auxiliary fuel. High operating costs.
|
|
Resource utilization |
Adjustable output ratio of gas, oil, and carbon based on customers’ needs and wastes properties. High adaptability and resources utilization level. |
Difficult to carry out process designs according to other raw materials and the diverse needs of customers.
|
Treatment objects: digestate, plastic,
straw, combustible garbage, industrial organic waste (including organic
hazardous waste), municipal sludge, paper sludge, oil sludge, etc.
Reactor types and features
|
Type |
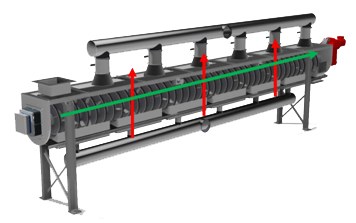
Spiral pyrolysis |
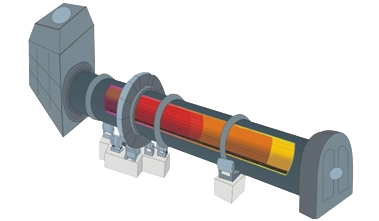
Rrotary kiln pyrolysis |
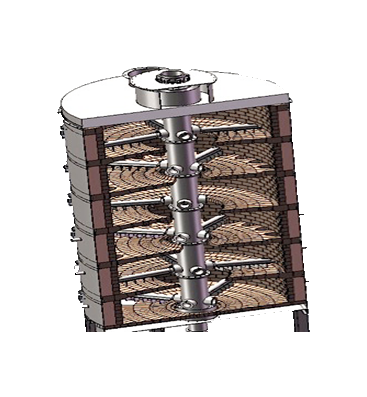
Multi-stage pyrolizer |
|
Application |
1) dispersing domestic waste. 2) industrial wastes. 3) carbon production from biomass. 4) some hazardous wastes.
|
1) tire cracking. |
1) sludge disposal. |
|
Features |
1) Easily controllable reaction time. 2) Efficient energy use, customized products according to demands. 3) Good sealing and improved environment & safety. 4) adjustable gaseous composition of the volatile matter. 5) not suitable for super-scale plants. |
1) wide application range, simple operation. |
1) Easily controllable reaction time. 2) wide application range. 3) vertical furnace, small land occupation. 4) Certain requirements on moisture content.
|
|
Picture |
|
|
|